1. FeatureTask
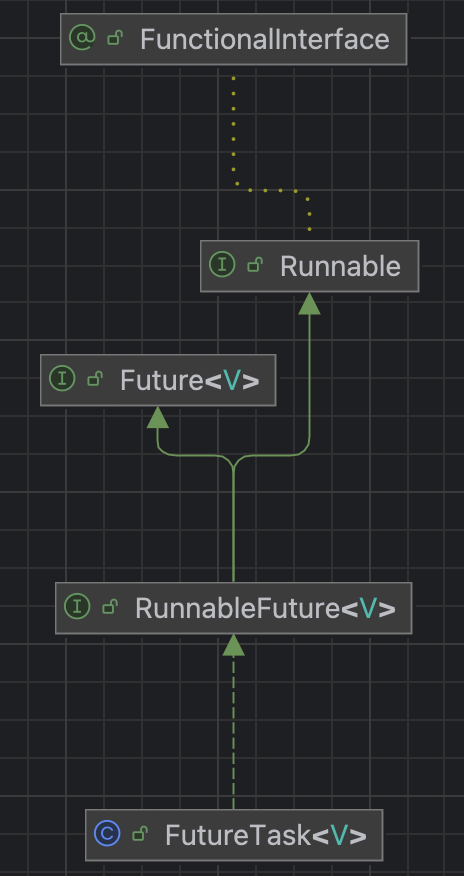
FutureTask是Runnable, Future接口的实现类;

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| {
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<String>( () -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t -----come in");
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "task over";
});
Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask, "t1");
t1.start();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t ----忙其它任务了");
while(true) {
if(futureTask.isDone()) {
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
break;
} else {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火");
}
}
}
|
运行结果
main —-忙其它任务了
t1 —–come in
正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火
正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火
正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火
正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火
正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火
正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火
正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火
正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火
正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火
正在处理中,不要再催了,越催越慢 ,再催熄火
task over
2. FeatureTask配合线程池使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
FutureTask<String> futureTask1 = new FutureTask<String>(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "task1 over";
});
threadPool.submit(futureTask1);
FutureTask<String> futureTask2 = new FutureTask<String>(() -> {
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "task2 over";
});
threadPool.submit(futureTask2);
System.out.println(futureTask1.get());
System.out.println(futureTask2.get());
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t -----end");
threadPool.shutdown();
}
|
运行结果
task1 over
task2 over
—-costTime: 830 毫秒
main —–end
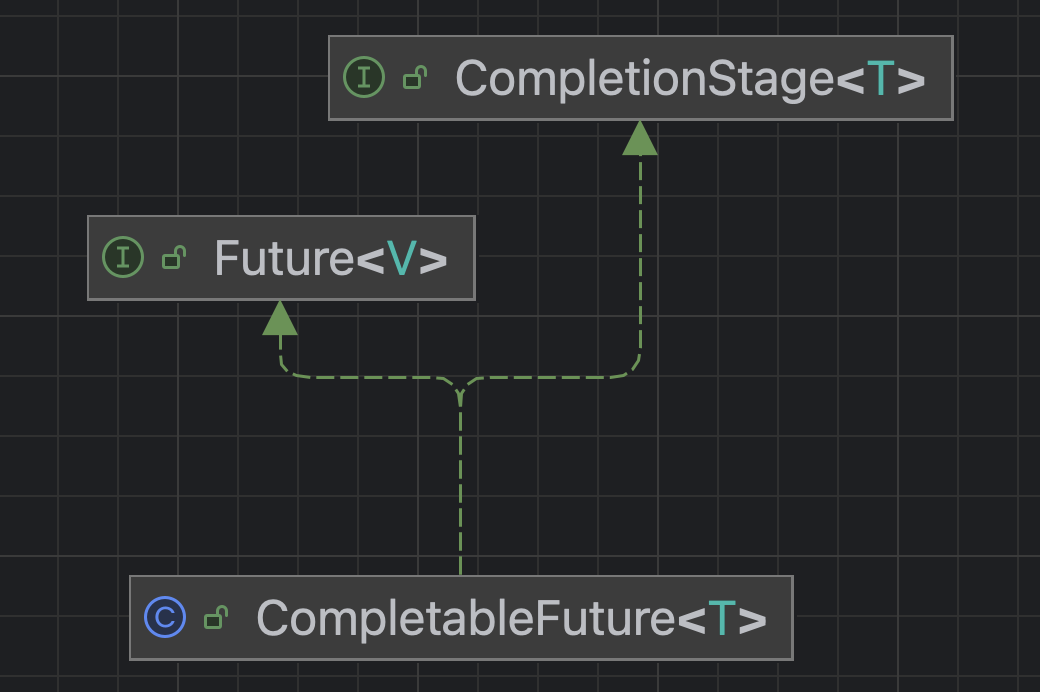
3. CompletableFuture

1
2
3
4
5
6
|
private static final boolean useCommonPool =
(ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism() > 1);
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
|

描述串行关系,主要是 thenApply、thenAccept、thenRun 和 thenCompose 这四个系列的接口。
- thenApply 系列函数里参数 fn 的类型是接口 Function<T, R>,这个接口里与 CompletionStage 相关的方法是 R apply(T t),这个方法既能接收参数也支持返回值,所以 thenApply 系列方法返回的是CompletionStage。
- thenAccept 系列方法里参数 consumer 的类型是接口Consumer,这个接口里与 CompletionStage 相关的方法是 void accept(T t),这个方法虽然支持参数,但却不支持回值,所以 thenAccept 系列方法返回的是CompletionStage。
- thenRun 系列方法里 action 的参数是 Runnable,所以 action 既不能接收参数也不支持返回值,所以 thenRun 系列方法返回的也是CompletionStage。
- 这些方法里面 Async 代表的是异步执行 fn、consumer 或者 action。其中 thenCompose 系列方法,这个系列的方法会新创建出一个子流程,最终结果和 thenApply 系列是相同的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 1;
}).thenApply(f ->{
return f + 2;
}).thenApply(f ->{
return f + 3;
}).thenAccept(System.out::println);
|
- 描述AND汇聚关系,主要是 thenCombine、thenAcceptBoth 和 runAfterBoth 系列的接口。这些接口的区别也是源自 fn、consumer、action 这三个核心参数不同。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t ---启动");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 10;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t ---启动");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 20;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = completableFuture1.thenCombine(completableFuture2, (x, y) -> {
System.out.println("-----开始两个结果合并");
return x + y;
});
System.out.println(result.join());
|
- 描述OR汇聚关系,主要是 applyToEither、acceptEither 和 runAfterEither 系列的接口,这些接口的区别也是源自 fn、consumer、action 这三个核心参数不同。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| CompletableFuture<String> playA = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("A come in");
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "playA";
});
CompletableFuture<String> playB = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("B come in");
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "playB";
});
CompletableFuture<String> result = playA.applyToEither(playB, f -> {
return f + " is winer";
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"-----: "+result.join());
|
- 异常处理,主要是exceptionally、whencomplete、whencompleteAsync、handle、handleAsync接口,类比try{}catch{}中的 catch{}、try{}finally{}中的 finally{}。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("111");
return 1;
},threadPool).handle((f,e) -> {
System.out.println("222");
return f + 2;
}).handle((f,e) -> {
System.out.println("333");
return f + 3;
}).whenComplete((v,e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("----计算结果: "+v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return null;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"----主线程先去忙其它任务");
threadPool.shutdown();
}
|
4. CompletableFuture搭配线程池使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "hello supplyAsync";
},threadPool);
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
threadPool.shutdown();
}
|