1. springboot启动类加载
首先加载springBoot启动类注入到spring容器中beanDefinitionMap中,看下prepareContext方法中的load方法:load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
跟进该方法最终会执行BeanDefinitionLoader的load方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| private int load(Object source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
//如果是class类型,启用注解类型
if (source instanceof Class<?>) {
return load((Class<?>) source);
}
//如果是resource类型,启用xml解析
if (source instanceof Resource) {
return load((Resource) source);
}
//如果是package类型,启用扫描包,例如:@ComponentScan
if (source instanceof Package) {
return load((Package) source);
}
//如果是字符串类型,直接加载
if (source instanceof CharSequence) {
return load((CharSequence) source);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass());
}
|
继续跟进load(Class<?> source)方法:
上述方法判断启动类中是否包含@component注解,可我们的启动类并没有该注解。继续跟进会发现,AnnotationUtils判断是否包含该注解是通过递归实现,注解上的注解若包含指定类型也是可以的。
启动类中包含@SpringBootApplication注解,进一步查找到@SpringBootConfiguration注解,然后查找到@Component注解,最后会查找到@Component注解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration {
}
|
在查找到@Component注解后,表面该对象为spring bean,然后会将其信息包装成 beanDefinitaion ,添加到容器的 beanDefinitionMap中。如下:
如此一来,我们的启动类就被包装成AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition了,后续启动类的处理都基于该对象了。
2. @EnableAutoConfiguration
@SpringBootApplication注解中包含了自动配置的入口注解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {}
|
我们跟进去看看**@EnableAutoConfiguration**
1
2
3
| @AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {}
|
2.1 @AutoConfigurationPackage
1
2
| @Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {}
|
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class):默认将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication)所在的包及其子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器中。如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//默认将会扫描@SpringBootApplication标注的主配置类所在的包及其子包下所有组件
register(registry, new PackageImport(metadata).getPackageName());
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.<Object>singleton(new PackageImport(metadata));
}
}
|
2.2 @Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector: 导入哪些组件的选择器,将所有需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回,这些组件就会被添加到容器中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| //EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector的父类:AutoConfigurationImportSelector
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
try {
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
configurations = sort(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return configurations.toArray(new String[configurations.size()]);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
|
我们主要看第11行List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);会给容器中注入众多的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration),就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件,并配置好这些组件。获取这些组件后,还要过滤一下这些组件,我们跟进去看看
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
//...
return configurations;
}
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
try {
//从类路径的META-INF/spring.factories中加载所有默认的自动配置类
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
//获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的所有值,也就是EnableAutoConfiguration.class的值
String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
}
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() + "] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
|
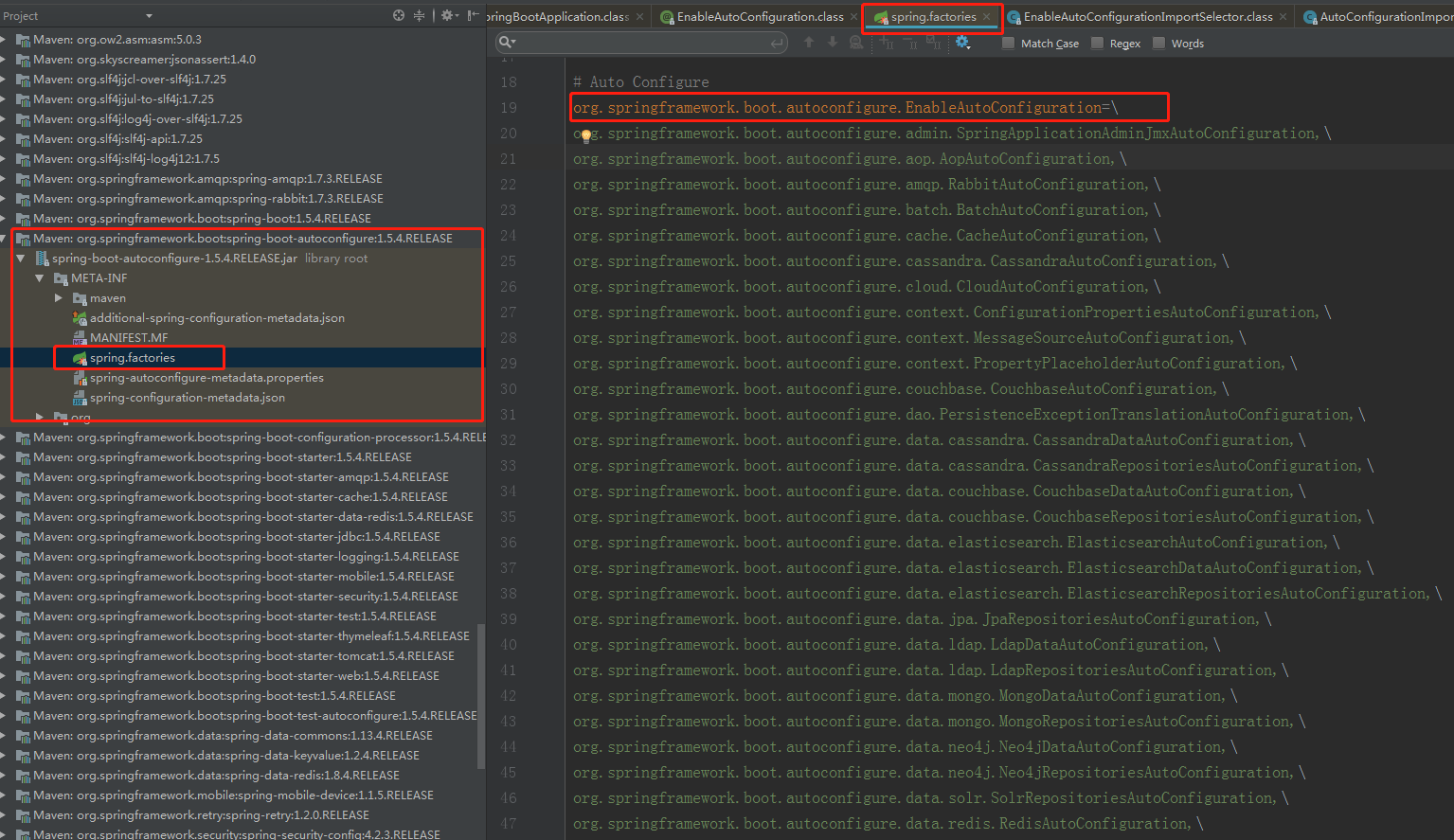
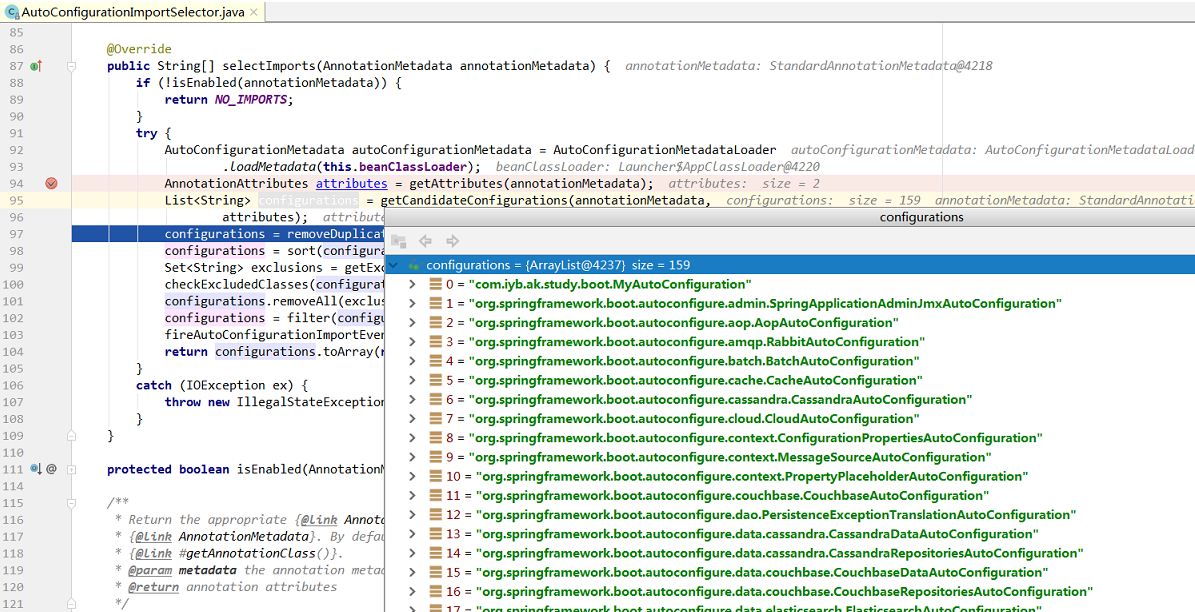
SpringBoot启动的时候从类路径下的 META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值,并将这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中,自动配置类就会生效,最后完成自动配置工作。EnableAutoConfiguration默认在spring-boot-autoconfigure这个包中,如下图
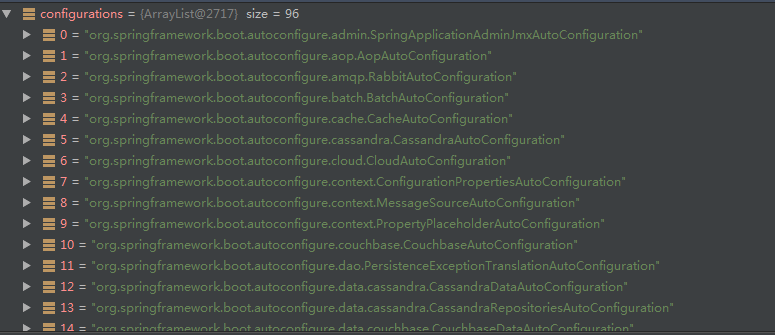
最终有96个自动配置类被加载并注册进Spring容器中
我们也可以将需要自动配置的Bean写入这个文件
3. 自定义starter
首先定义一个配置类模块:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "enabled.autoConfituration", matchIfMissing = true)
public class MyAutoConfiguration {
static {
System.out.println("myAutoConfiguration init...");
}
@Bean
public SimpleBean simpleBean(){
return new SimpleBean();
}
}
|
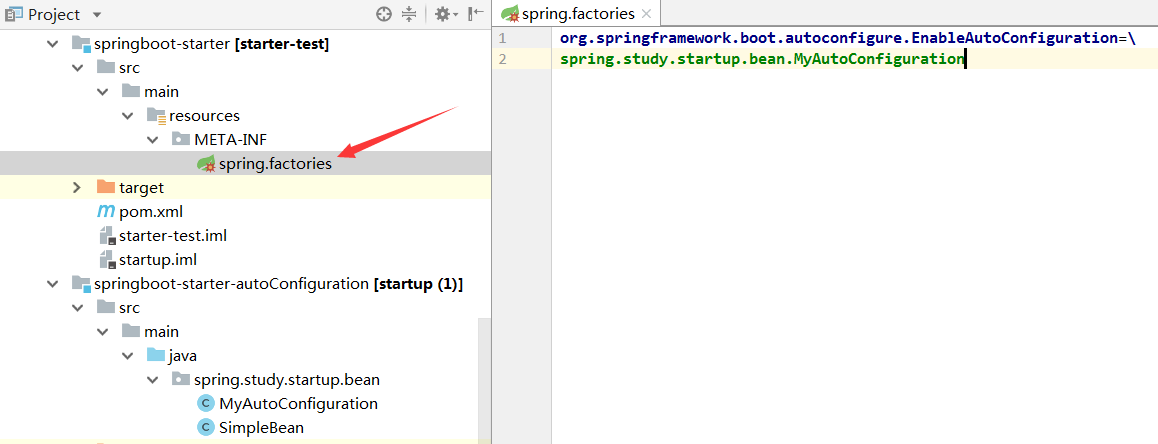
然后定义一个starter模块,里面无需任何代码,pom也无需任何依赖,只需在META-INF下面建一个 spring.factories文件,添加如下配置:
1
2
| org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
spring.study.startup.bean.MyAutoConfiguration
|
最后只需在启动类项目的pom中引入我们的 starter 模块即可。
3.1 原理
最终在AutoConfigurationImportSelector解析spring.factories文件:
springBoot为我们提供的配置类有180多个,但是我们不可能会全部引入。按条件注解 @Conditional或者@ConditionalOnProperty等相关注解进行判断,决定是否需要装配。
我们自定义的配置类也是以相同的逻辑进行装配,我们指定了以下注解:
1
| @ConditionalOnProperty(name = "enabled.autoConfituration", matchIfMissing = true)
|
默认为 true,所以自定义的starter成功执行。