经常需要将配置信息配置在properties文件中,然后在XML文件中以占位符的方式引用。
实现思路很简单,在bean实例化之前,编辑BeanDefinition,解析XML文件中的占位符,然后用properties文件中的配置值替换占位符。而BeanFactoryPostProcessor具有编辑BeanDefinition的能力,因此PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer继承自BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
测试: car.properties
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:car.properties" />
</bean>
<bean id="car" class="org.springframework.test.bean.Car">
<property name="brand" value="${brand}" />
</bean>
</beans>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class PropertyPlaceholderConfigurerTest {
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:property-placeholder-configurer.xml");
Car car = applicationContext.getBean("car", Car.class);
assertThat(car.getBrand()).isEqualTo("lamborghini");
}
}
|
包扫描
结合bean的生命周期,包扫描只不过是扫描特定注解的类,提取类的相关信息组装成BeanDefinition注册到容器中。
在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中解析<context:component-scan />标签,扫描类组装BeanDefinition然后注册到容器中的操作在ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan中实现。
测试:
1
2
3
4
| @Component
public class Car {
}
|
package-scan.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="org.springframework.test.bean"/>
</beans>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class PackageScanTest {
@Test
public void testScanPackage() throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:package-scan.xml");
Car car = applicationContext.getBean("car", Car.class);
assertThat(car).isNotNull();
}
}
|
@Value注解
注解@Value和@Autowired通过BeanPostProcessor处理。InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor增加postProcessPropertyValues方法,在bean实例化之后设置属性之前执行,查看AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean方法。
增加AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor用于处理注解@Value,@Autowired的处理在下一节实现,在ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan将其添加到容器中。查看AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues,其中字符解析器StringValueResolver在PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer中添加到BeanFactory中。
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Component
public class Car {
@Value("${brand}")
private String brand;
}
|
value-annotation.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:car.properties" />
</bean>
<context:component-scan base-package="org.springframework.test.bean"/>
</beans>
|
car.properties
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class ValueAnnotationTest {
@Test
public void testValueAnnotation() throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:value-annotation.xml");
Car car = applicationContext.getBean("car", Car.class);
assertThat(car.getBrand()).isEqualTo("lamborghini");
}
}
|
@Autowired注解
@Autowired注解的处理见AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Component
public class Car {
}
@Component
public class Person implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
@Autowired
private Car car;
}
|
autowired-annotation.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="org.springframework.test.bean"/>
</beans>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class AutowiredAnnotationTest {
@Test
public void testAutowiredAnnotation() throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:autowired-annotation.xml");
Person person = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
assertThat(person.getCar()).isNotNull();
}
}
|
bugfix:没有为代理bean设置属性
问题现象:没有为代理bean设置属性
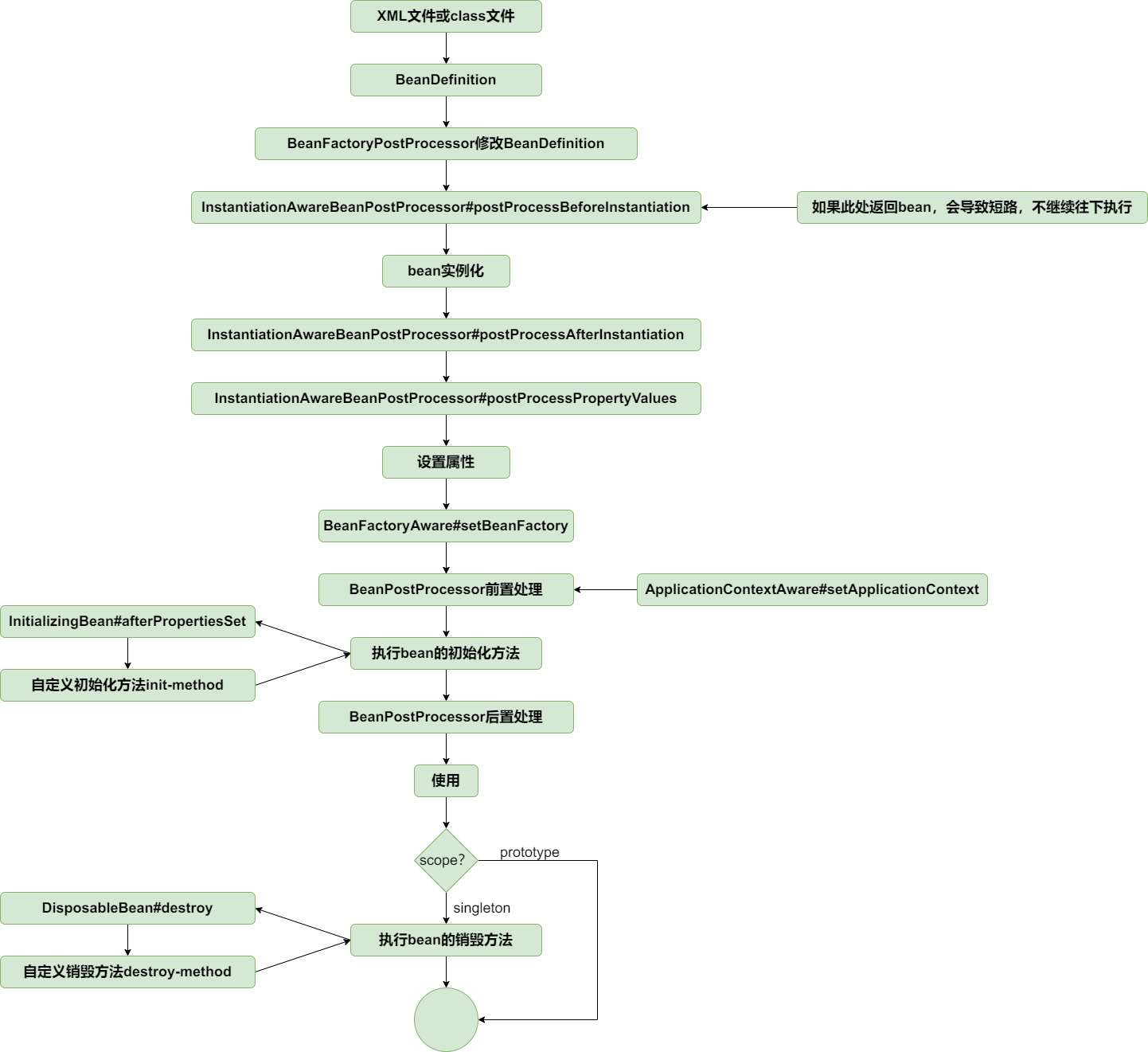
问题原因:织入逻辑在InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation中执行,而该方法如果返回非null,会导致”短路”,不会执行后面的设置属性逻辑。因此如果该方法中返回代理bean后,不会为代理bean设置属性。
修复方案:跟spring保持一致,将织入逻辑迁移到BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization,即将DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#postProcessBeforeInstantiation的内容迁移到DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization中。
顺便完善spring的扩展机制,为InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor增加postProcessAfterInstantiation方法,该方法在bean实例化之后设置属性之前执行。
至此,bean的生命周期比较完整了,如下:
测试: populate-proxy-bean-with-property-values.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<bean id="worldService" class="org.springframework.test.service.WorldServiceImpl">
<property name="name" value="earth"/>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"/>
<bean id="pointcutAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="expression" value="execution(* org.springframework.test.service.WorldService.explode(..))"/>
<property name="advice" ref="methodInterceptor"/>
</bean>
<bean id="methodInterceptor" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.adapter.MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor">
<property name="advice" ref="beforeAdvice"/>
</bean>
<bean id="beforeAdvice" class="org.springframework.test.common.WorldServiceBeforeAdvice"/>
</beans>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class WorldServiceImpl implements WorldService {
private String name;
@Override
public void explode() {
System.out.println("The " + name + " is going to explode");
}
//setter and getter
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class AutoProxyTest {
@Test
public void testPopulateProxyBeanWithPropertyValues() throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:populate-proxy-bean-with-property-values.xml");
//获取代理对象
WorldService worldService = applicationContext.getBean("worldService", WorldService.class);
worldService.explode();
assertThat(worldService.getName()).isEqualTo("earth");
}
}
|
类型转换(一)
spring在org.springframework.core.convert.converter包中定义了三种类型转换器接口:Converter、ConverterFactory、GenericConverter。
一、Converter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public interface Converter<S, T> {
/**
* 类型转换
*/
T convert(S source);
}
|
Converter能将S类型的对象转换为T类型的对象,比如将String类型的对象转换为Integer类型的对象的实现类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public class StringToIntegerConverter implements Converter<String, Integer> {
@Override
public Integer convert(String source) {
return Integer.valueOf(source);
}
}
|
使用:
1
| Integer num = new StringToIntegerConverter().convert("8888");
|
二、ConverterFactory
1
2
3
4
| public interface ConverterFactory<S, R> {
<T extends R> Converter<S, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType);
}
|
Converter<S,T>接口适合一对一的类型转换,如果要将String类型转换为Ineger/Long/Float/Double/Decimal等类型,就要实现一系列的StringToInteger/StringToLongConverter/StringToFloatConverter转换器,非常不优雅。
ConverterFactory接口则适合一对多的类型转换,可以将一种类型转换为另一种类型及其子类。比如将String类型转换为Ineger/Long/Float/Double/Decimal等Number类型时,只需定义一个ConverterFactory转换器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public class StringToNumberConverterFactory implements ConverterFactory<String, Number> {
@Override
public <T extends Number> Converter<String, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType) {
return new StringToNumber<T>(targetType);
}
private static final class StringToNumber<T extends Number> implements Converter<String, T> {
private final Class<T> targetType;
public StringToNumber(Class<T> targetType) {
this.targetType = targetType;
}
@Override
public T convert(String source) {
if (source.length() == 0) {
return null;
}
if (targetType.equals(Integer.class)) {
return (T) Integer.valueOf(source);
} else if (targetType.equals(Long.class)) {
return (T) Long.valueOf(source);
}
//TODO 其他数字类型
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot convert String [" + source + "] to target class [" + targetType.getName() + "]");
}
}
}
}
|
使用:
1
2
3
| StringToNumberConverterFactory converterFactory = new StringToNumberConverterFactory();
Converter<String, Integer> stringToIntegerConverter = converterFactory.getConverter(Integer.class);
Integer num = stringToIntegerConverter.convert("8888");
|
三、GenericConverter
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public interface GenericConverter {
Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes();
Object convert(Object source, Class sourceType, Class targetType);
}
|
String类型转换为Boolean类型的实现类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class StringToBooleanConverter implements GenericConverter {
@Override
public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {
return Collections.singleton(new ConvertiblePair(String.class, Boolean.class));
}
@Override
public Object convert(Object source, Class sourceType, Class targetType) {
return Boolean.valueOf((String) source);
}
}
|
使用:
1
| Boolean flag = new StringToBooleanConverter().convert("true", String.class, Boolean.class);
|
ConversionService是类型转换体系的核心接口,将以上三种类型转换器整合到一起,GenericConversionService是其实现类,DefaultConversionService在GenericConversionService的基础上添加内置转换器。
测试见TypeConversionFirstPartTest。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| public class TypeConversionFirstPartTest {
@Test
public void testStringToIntegerConverter() throws Exception {
StringToIntegerConverter converter = new StringToIntegerConverter();
Integer num = converter.convert("8888");
assertThat(num).isEqualTo(8888);
}
@Test
public void testStringToNumberConverterFactory() throws Exception {
StringToNumberConverterFactory converterFactory = new StringToNumberConverterFactory();
Converter<String, Integer> stringToIntegerConverter = converterFactory.getConverter(Integer.class);
Integer intNum = stringToIntegerConverter.convert("8888");
assertThat(intNum).isEqualTo(8888);
Converter<String, Long> stringToLongConverter = converterFactory.getConverter(Long.class);
Long longNum = stringToLongConverter.convert("8888");
assertThat(longNum).isEqualTo(8888L);
}
@Test
public void testGenericConverter() throws Exception {
StringToBooleanConverter converter = new StringToBooleanConverter();
Boolean flag = (Boolean) converter.convert("true", String.class, Boolean.class);
assertThat(flag).isTrue();
}
@Test
public void testGenericConversionService() throws Exception {
GenericConversionService conversionService = new GenericConversionService();
conversionService.addConverter(new StringToIntegerConverter());
Integer intNum = conversionService.convert("8888", Integer.class);
assertThat(conversionService.canConvert(String.class, Integer.class)).isTrue();
assertThat(intNum).isEqualTo(8888);
conversionService.addConverterFactory(new StringToNumberConverterFactory());
assertThat(conversionService.canConvert(String.class, Long.class)).isTrue();
Long longNum = conversionService.convert("8888", Long.class);
assertThat(longNum).isEqualTo(8888L);
conversionService.addConverter(new StringToBooleanConverter());
assertThat(conversionService.canConvert(String.class, Boolean.class)).isTrue();
Boolean flag = conversionService.convert("true", Boolean.class);
assertThat(flag).isTrue();
}
}
|
类型转换(二)
上一节实现了spring中的类型转换体系,本节将类型转换的能力整合到容器中。
为了方便使用,提供了创建ConversionService的FactoryBean——ConversionServiceFactoryBean。
如果有定义ConversionService,在AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法中设置到容器中。
类型转换的时机有两个:
- 为bean填充属性时,见AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyPropertyValues
- 处理@Value注解时,见AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues
你可能会有疑问,如果没有定义ConversionService,是怎么进行基本类型的转换的?其实spring为了向下兼容保留了一套比较旧的类型转换机制,没有定义ConversionService时会使用其进行基本类型的转换工作,不必关注旧的类型转换机制。
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public class Car {
private int price;
private LocalDate produceDate;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class StringToLocalDateConverter implements Converter<String, LocalDate> {
private final DateTimeFormatter DATE_TIME_FORMATTER;
public StringToLocalDateConverter(String pattern) {
DATE_TIME_FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(pattern);
}
@Override
public LocalDate convert(String source) {
return LocalDate.parse(source, DATE_TIME_FORMATTER);
}
}
|
type-conversion-second-part.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<bean id="car" class="org.springframework.test.bean.Car">
<property name="price" value="1000000"/>
<property name="produceDate" value="2021-01-01"/>
</bean>
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters" ref="converters"/>
</bean>
<bean id="converters" class="org.springframework.test.common.ConvertersFactoryBean"/>
</beans>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class TypeConversionSecondPartTest {
@Test
public void testConversionService() throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:type-conversion-second-part.xml");
Car car = applicationContext.getBean("car", Car.class);
assertThat(car.getPrice()).isEqualTo(1000000);
assertThat(car.getProduceDate()).isEqualTo(LocalDate.of(2021, 1, 1));
}
}
|