解决循环依赖问题:没有代理对象 先理解spring中为什么会有循环依赖的问题。比如如下的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class A { private B b; //getter and setter }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class B { private A a; //getter and setter }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <beans> <bean id="a" class="org.springframework.test.bean.A"> <property name="b" ref="b"/> </bean> <bean id="b" class="org.springframework.test.bean.B"> <property name="a" ref="a"/> </bean> </beans>
A依赖B,B又依赖A,循环依赖。容器加载时会执行依赖流程:
实例化A,发现依赖B,然后实例化B
实例化B,发现依赖A,然后实例化A
实例化A,发现依赖B,然后实例化B
…
死循环直至栈溢出。
解决该问题的关键在于何时将实例化后的bean放进容器中,设置属性前还是设置属性后。现有的执行流程,bean实例化后并且设置属性后会被放进singletonObjects单例缓存中。如果我们调整一下顺序,当bean实例化后就放进singletonObjects单例缓存中,提前暴露引用,然后再设置属性,就能解决上面的循环依赖问题,执行流程变为:
步骤一:getBean(a),检查singletonObjects是否包含a,singletonObjects不包含a,实例化A放进singletonObjects,设置属性b,发现依赖B,尝试getBean(b)
步骤二:getBean(b),检查singletonObjects是否包含b,singletonObjects不包含b,实例化B放进singletonObjects,设置属性a,发现依赖A,尝试getBean(a)
步骤三:getBean(a),检查singletonObjects是否包含a,singletonObjects包含a,返回a
步骤四:步骤二中的b拿到a,设置属性a,然后返回b
步骤五:步骤一中的a拿到b,设置属性b,然后返回a
可见调整bean放进singletonObjects(人称一级缓存)的时机到bean实例化后即可解决循环依赖问题。但为了和spring保持一致,我们增加一个二级缓存earlySingletonObjects,在bean实例化后将bean放进earlySingletonObjects中(见AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean方法第6行),getBean()时检查一级缓存singletonObjects和二级缓存earlySingletonObjects中是否包含该bean,包含则直接返回(见AbstractBeanFactory#getBean第1行)。
单测见CircularReferenceWithoutProxyBeanTest#testCircularReference。
增加二级缓存,不能解决有代理对象时的循环依赖。原因是放进二级缓存earlySingletonObjects中的bean是实例化后的bean,而放进一级缓存singletonObjects中的bean是代理对象(代理对象在BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization中返回),两个缓存中的bean不一致。比如上面的例子,如果A被代理,那么B拿到的a是实例化后的A,而a是被代理后的对象,即b.getA() != a,
解决循环依赖问题:有代理对象 解决有代理对象时的循环依赖问题,需要提前暴露代理对象的引用,而不是暴露实例化后的bean的引用(这是上节的遗留问题的原因,应该提前暴露A的代理对象的引用)。
spring中用singletonFactories(一般称第三级缓存)解决有代理对象时的循环依赖问题。在实例化后提前暴露代理对象的引用(见AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean方法第6行)。
getBean()时依次检查一级缓存singletonObjects、二级缓存earlySingletonObjects和三级缓存singletonFactories中是否包含该bean。如果三级缓存中包含该bean,则挪至二级缓存中,然后直接返回该bean。见AbstractBeanFactory#getBean方法第1行。
最后将代理bean放进一级缓存singletonObjects,见AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory第104行。
单测见CircularReferenceWithProxyBeanTest。
懒加载 事实上,并不是所有的bean在初始化容器的时候都会创建。随着项目规模的不断扩大,bean的数目也越来越多。如果每次启动容器都需要加载大量的bean,这无疑会带来大量的资源浪费。所有spring提供了懒加载机制,我们可以将我们认为暂时用不到的bean设为懒加载,这样只有在我们需要这个bean的时候这个bean才会被创建。
测试:
lazy-test.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 //只有当bean是单例且不为懒加载才会被创建 public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException { beanDefinitionMap.forEach((beanName, beanDefinition) -> { if(beanDefinition.isSingleton()&&!beanDefinition.isLazyInit()){ getBean(beanName); } }); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class LazyInitTest { @Test public void testLazyInit() throws InterruptedException { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:lazy-test.xml"); System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+":applicationContext-over"); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); Car c= (Car) applicationContext.getBean("car"); c.showTime();//显示bean的创建时间 } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="org.springframework.test.bean.Car" lazyInit="true" init-method="init"> <property name="brand" value="porsche"/> </bean> </beans>
关闭懒加载的输出:
1 2 1671698959957:applicationContext-over 1671698959951:bean create
开启懒加载:
1 2 1671699030293:applicationContext-over 1671699031328:bean create
可以清楚的看到开启和不开启懒加载bean的创建时机的差异
多个切面匹配同一个方法 虽然在前面我们完成了对方法的增强,但并不完美。我们的目前的代码只能支持对方法的单个增强。作为spring的核心功能如果不支持多切面的话有点太别扭了。spring利用了拦截器链来完成了对多个切面的支持。
ProxyFactory 让我们从ProxyFactory开始,来看一下代理对象的整个创建流程。至于为什么从ProxyFactory开,这是因为代理对象最终是用ProxyFactory的getProxy()函数来获得的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class ProxyFactory extends AdvisedSupport{ public ProxyFactory() { } public Object getProxy() { return createAopProxy().getProxy(); } private AopProxy createAopProxy() { if (this.isProxyTargetClass()||this.getTargetSource().getTargetClass().length==0) { return new CglibAopProxy(this); } return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(this); } }
为了更贴合spring的实现,这里更改了ProxyFactory使其继承了AdvisedSupport,正如spring源码中做的那样。
基于JDK动态代理 ProxyFactory只是简单的做了下选择,当我们设置proxyTargetClass属性或者被代理对象没有接口时会调用cjlib动态代理,否则调用jdk动态代理。二者实现并没有太大区别,这里只贴出jdk动态代理的实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public Object getProxy() { return Proxy.newProxyInstance(getClass().getClassLoader(), advised.getTargetSource().getTargetClass(), this); } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { // 获取目标对象 Object target=advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(); Class<?> targetClass = target.getClass(); Object retVal = null; // 获取拦截器链 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); if(chain==null||chain.isEmpty()){ return method.invoke(target, args); }else{ // 将拦截器统一封装成ReflectiveMethodInvocation MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain. // 执行拦截器链 retVal = invocation.proceed(); } return retVal; }
jdk动态代理可以分为获取拦截器链,将拦截器统一封装成ReflectiveMethodInvocation,执行拦截器链三部分。我们来逐一看一下这三部分。
1.获取拦截器链 首先将获取到所有与当前method匹配的advice(增强),跟踪getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice代码,我们发现Spring AOP也使用缓存进行提高性能,如果该方法已经获取过拦截器,则直接取缓存,否则通过advisorChainFactory获取拦截器链。AdvisorChainFactory是用来获得拦截器链接口。它的一个实现类为DefaultAdvisorChainFactory
AdvisedSupport#getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) { Integer cacheKey=method.hashCode(); List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey); if (cached == null) { cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice( this, method, targetClass); this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached); } return cached; }
整体代码并不复杂,首先获取所有Advisor(切面),通过pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)校验当前代理对象是否匹配该Advisor,再通过pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher()校验是否匹配当前调用method。如果通过校验,则提取advisor中的interceptors增强,添加到interceptorList中。这里可能有读者会疑惑,我们明明是要获取MethodInterceptor,可AdvisedSupport的getAdvice()返回的是Advice(增强),其实如果我们点开MethodInterceptor的源码,我们会发现MethodInterceptor继承了Interceptor接口,而Interceptor又继承了Advice接口。因为这里的Advice和MethodInterceptor我们都是用的AOP联盟的接口,所以特此说明一下。
DefultAdvisorChainFactory#getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(AdvisedSupport config, Method method, Class<?> targetClass) { Advisor[] advisors = config.getAdvisors().toArray(new Advisor[0]); List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>(advisors.length); Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass()); for (Advisor advisor : advisors) { if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { // Add it conditionally. PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; // 校验当前Advisor是否适用于当前对象 if (pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher(); boolean match; // 校验Advisor是否应用到当前方法上 match = mm.matches(method,actualClass); if (match) { MethodInterceptor interceptor = (MethodInterceptor) advisor.getAdvice(); interceptorList.add(interceptor); } } } } return interceptorList; }
2.将拦截器封装成ReflectiveMethodInvocation 这里也是重写了ReflectiveMethodInvocation的实现,来支持多切面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public ReflectiveMethodInvocation(Object proxy,Object target, Method method, Object[] arguments,Class<?> targetClass,List<Object> chain) { this.proxy=proxy; this.target = target; this.method = method; this.arguments = arguments; this.targetClass=targetClass; this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers=chain; }
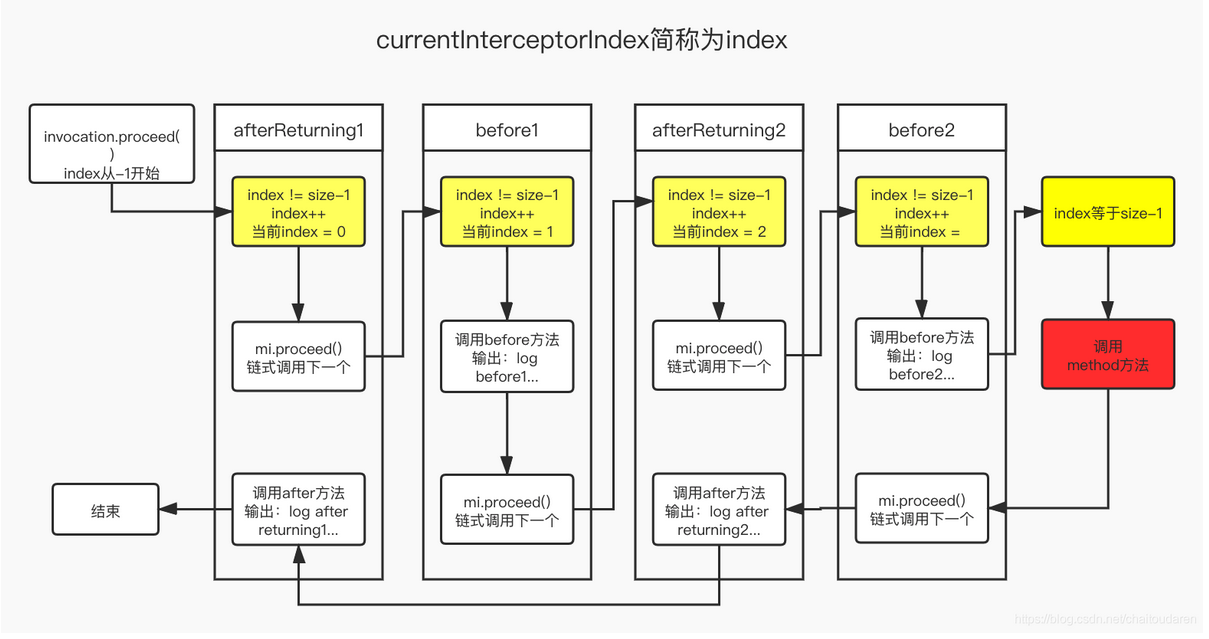
3.执行拦截器链 spring能够保证多个切面同时匹配同一方法的而不出现乱序的关键就在下面一段代码了。
ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public Object proceed() throws Throwable { // 初始currentInterceptorIndex为-1,每调用一次proceed就把currentInterceptorIndex+1 if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { // 当调用次数 = 拦截器个数时 // 触发当前method方法 return method.invoke(this.target, this.arguments); } Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex); // 普通拦截器,直接触发拦截器invoke方法 return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this); }
我们看到,MethodInvocation只是简单的将拦截器链的所有拦截器一一执行,最后再触发当前的method方法。这是很简单高效的方法,但问题是我们希望某些增强比如AfterReturningAdvice能够在方法执行完才被执行,这就涉及到不同增强的执行顺序的问题了。而MethodInvocation显然没有考虑顺序的问题,一个AfterReturningAdvice很可能在BeforeAdvice之前被调用。那么该如何保证顺序问题呢?
答案是,控制增强的调用顺序其实由每个拦截器负责,所以我们需要分析MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor和AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, BeforeAdvice { private MethodBeforeAdvice advice; public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor() { } public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) { this.advice = advice; } public void setAdvice(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) { this.advice = advice; } @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis()); return mi.proceed(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice { private AfterReturningAdvice advice; public AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor() { } public AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(AfterReturningAdvice advice) { this.advice = advice; } @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { Object retVal = mi.proceed(); this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis()); return retVal; } }
看了源码大家应该就清楚了,拦截器链执行的顺序正时在各个拦截器的invoke方法中实现的。before会先执行advice增强方法再链式调用,这个比较好理解而after则是先执行链式调用,再调用advice增强方法,也就是一个递归的过程。和二叉树的遍历有些异曲同工之处。
测试 !!!!!!!注意,使用过高版本的java可以因为java版本和cjlib冲突导致报错。建议使用java8进行测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class WorldServiceImpl implements WorldService { private String name; @Override public void explode() { System.out.println("The " + name + " is going to explode"); } @Override public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
前置增强:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class WorldServiceBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice { @Override public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println("BeforeAdvice: do something before the earth explodes"); } }
后置返回增强:
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class WorldServiceAfterReturnAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice { @Override public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println("AfterAdvice: do something after the earth explodes"); } }
测试代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class ProxyFactoryTest { @Test public void testAdvisor() throws Exception { WorldService worldService = new WorldServiceImpl(); //Advisor是Pointcut和Advice的组合 String expression = "execution(* org.springframework.test.service.WorldService.explode(..))"; //第一个切面 AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor advisor = new AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor(); advisor.setExpression(expression); MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor methodInterceptor = new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(new WorldServiceBeforeAdvice()); advisor.setAdvice(methodInterceptor); //第二个切面 AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor advisor1=new AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor(); advisor1.setExpression(expression); AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor afterReturningAdviceInterceptor=new AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(new WorldServiceAfterReturnAdvice()); advisor1.setAdvice(afterReturningAdviceInterceptor); //通过ProxyFactory来获得代理 ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(); TargetSource targetSource = new TargetSource(worldService); factory.setTargetSource(targetSource); factory.setProxyTargetClass(true); factory.addAdvisor(advisor); factory.addAdvisor(advisor1); WorldService proxy = (WorldService) factory.getProxy(); proxy.explode(); } }
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 BeforeAdvice: do something before the earth explodes The null is going to explode AfterAdvice: do something after the earth explodes 进程已结束,退出代码为 0
多切面动态代理融入bean生命周期 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void testAutoProxy() throws Exception { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:auto-proxy.xml"); //获取代理对象 WorldService worldService = applicationContext.getBean("worldService", WorldService.class); worldService.explode(); }
auto-proxy.xml:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <bean id="worldService" class="org.springframework.test.service.WorldServiceImpl"/> <bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"/> <bean id="pointcutAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor"> <property name="expression" value="execution(* org.springframework.test.service.WorldService.explode(..))"/> <property name="advice" ref="methodInterceptor"/> </bean> <bean id="pointcutAdvisor2" class="org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor"> <property name="expression" value="execution(* org.springframework.test.service.WorldService.explode(..))"/> <property name="advice" ref="methodInterceptor2"/> </bean> <bean id="methodInterceptor" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.adapter.MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor"> <property name="advice" ref="beforeAdvice"/> </bean> <bean id="methodInterceptor2" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.adapter.AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor"> <property name="advice" ref="afterAdvice"/> </bean> <bean id="afterAdvice" class="org.springframework.test.common.WorldServiceAfterReturnAdvice"/> <bean id="beforeAdvice" class="org.springframework.test.common.WorldServiceBeforeAdvice"/> </beans>
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 BeforeAdvice: do something before the earth explodes The null is going to explode AfterAdvice: do something after the earth explodes 进程已结束,退出代码为 0
至此,我们已经解决多切面匹配同一方法的问题。