1. 基础配置 ⽣产者发送消息的示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer (PRODUCER_GROUP);producer.setNamesrvAddr("name-server1-ip:9876;name-server2-ip:9876" ); producer.start(); Message msg = new Message (TOPIC,TAG,("Hello RocketMQ " + i).getBytes(RemotingHelper.*DEFAULT_CHARSET*));msg.setKeys("" ); SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg);producer.send(msg, new SendCallback () { @Override public void onSuccess (SendResult sendResult) { } @Override public void onException (Throwable e) { } }); producer.sendOneway(msg);
发送流程如下:
1、初始化默认⽣产者,传递参数⽣产者组名;
2、设置名字服务地址 ;
3、启动⽣产者服务;
4、定义消息对象 ;
5、⽣产者⽀持普通发送、oneway 发送、异步回调 三种⽅式发送消息 。
2. 发送消息流程 2.1 构造函数 构造函数包含两个部分:
初始化实现类 DefaultMQProducerImpl ;
根据是否开启消息轨迹参数 enableMsgTrace 判断是否增加消息轨迹逻辑 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 private String producerGroup;private int sendMsgTimeout = 3000 ;protected final transient DefaultMQProducerImpl defaultMQProducerImpl;public DefaultMQProducer (final String namespace, final String producerGroup, RPCHook rpcHook, boolean enableMsgTrace, final String customizedTraceTopic) { this .namespace = namespace; this .producerGroup = producerGroup; defaultMQProducerImpl = new DefaultMQProducerImpl (this , rpcHook); if (enableMsgTrace) { try { AsyncTraceDispatcher dispatcher = new AsyncTraceDispatcher (producerGroup, TraceDispatcher.Type.PRODUCE, customizedTraceTopic, rpcHook); dispatcher.setHostProducer(this .defaultMQProducerImpl); traceDispatcher = dispatcher; this .defaultMQProducerImpl.registerSendMessageHook( new SendMessageTraceHookImpl (traceDispatcher)); this .defaultMQProducerImpl.registerEndTransactionHook( new EndTransactionTraceHookImpl (traceDispatcher)); } catch (Throwable e) { log.error("system mqtrace hook init failed ,maybe can't send msg trace data" ); } } }
2.2 启动生产者 DefaultMQProducer 类的 start ⽅法,本质上是调⽤包装类 DefaultMQProducerImpl 的 start ⽅法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public void start () throws MQClientException { this .setProducerGroup(withNamespace(this .producerGroup)); this .defaultMQProducerImpl.start(); if (null != traceDispatcher) { try { traceDispatcher.start(this .getNamesrvAddr(), this .getAccessChannel()); } catch (MQClientException e) { log.warn("trace dispatcher start failed " , e); } } }
进⼊ DefaultMQProducerImpl 类,查看该类的逻辑 。
2.2.1 检测配置 判断⽣产者组是否合法,⽣产者名称不能和默认⽣产者组名称相同。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 private void checkConfig () throws MQClientException { Validators.checkGroup(this .defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup()); if (null == this .defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup()) { throw new MQClientException ("producerGroup is null" , null ); } if (this .defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup().equals(MixAll.DEFAULT_PRODUCER_GROUP)) { throw new MQClientException ("producerGroup can not equal " + MixAll.DEFAULT_PRODUCER_GROUP + ", please specify another one." , null ); } }
2.2.2 创建客户端实例 1 this .mQClientFactory = MQClientManager.getInstance().getOrCreateMQClientInstance(this .defaultMQProducer, rpcHook);
MQClientInstance 对象通过 MQClientManager 这个单例类创建 ,标志着⼀个客户端实例,是⾮常核⼼的类,每⼀个实例对象有⼀个唯⼀的 clientId 。
1 2 3 private final ConcurrentMap<String, MQProducerInner> producerTable = new ConcurrentHashMap <String, MQProducerInner>();private final ConcurrentMap<String, MQConsumerInner> consumerTable = new ConcurrentHashMap <String, MQConsumerInner>();private final ConcurrentMap<String, MQAdminExtInner> adminExtTable = new ConcurrentHashMap <String, MQAdminExtInner>();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private final ConcurrentMap<String, TopicRouteData> topicRouteTable = new ConcurrentHashMap <String, TopicRouteData>();private final ConcurrentMap<String, HashMap<Long, String>> brokerAddrTable = new ConcurrentHashMap <String, HashMap<Long, String>>(); private final ConcurrentMap<String, HashMap<String, Integer>> brokerVersionTable = new ConcurrentHashMap <String, HashMap<String, Integer>>();
2.2.3 注册本地生产者 1 boolean registerOK = mQClientFactory.registerProducer(this .defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup(), this );
注册本地⽣产者的本质是修改客户端实例的⽣产者表引⽤:
1 MQProducerInner prev = this .producerTable.putIfAbsent(group, producer);
2.2.4 启动客户端实例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 mQClientFactory.start(); public void start () throws MQClientException { synchronized (this ) { switch (this .serviceState) { case CREATE_JUST: this .serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED; if (null == this .clientConfig.getNamesrvAddr()) { this .mQClientAPIImpl.fetchNameServerAddr(); } this .mQClientAPIImpl.start(); this .startScheduledTask(); this .pullMessageService.start(); this .rebalanceService.start(); this .defaultMQProducer.getDefaultMQProducerImpl().start(false ); log.info("the client factory [{}] start OK" , this .clientId); this .serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING; break ; case START_FAILED: throw new MQClientException ("The Factory object[" + this .getClientId() + "] has been created before, and failed." , null ); default : break ; } } }
实例启动后,会启动通讯模块、定时任务、负载均衡服务、消费者拉取服务 。
重点看定时任务 startScheduledTask ⽅法 , 定时任务代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 MQClientInstance.this .updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(); MQClientInstance.this .cleanOfflineBroker(); MQClientInstance.this .sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock(); MQClientInstance.this .persistAllConsumerOffset();
发送心跳:定时任务每隔30s将客户端信息发送到broker.
1 2 3 4 5 public class HeartbeatData extends RemotingSerializable { private String clientID; private Set<ProducerData> producerDataSet = new HashSet <ProducerData>(); private Set<ConsumerData> consumerDataSet = new HashSet <ConsumerData>(); }
当 Broker 收到⼼跳请求之后,会通过⽣产者管理器 ProducerManager 、消费者管理器 ConsumerManager 分别更新⽣ 产者客户端缓存、消费者客户端缓存。
对于⽣产者来讲,它需要知道需要发送消息的主题对应的路由信息 , 因此需要定时更新路由信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class TopicRouteData extends RemotingSerializable { private String orderTopicConf; private List<QueueData> queueDatas; private List<BrokerData> brokerDatas; private HashMap<String, List<String>> filterServerTable; } topicRouteData = this .mQClientAPIImpl.getDefaultTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(defaultMQProducer.getCreateTopicKey(),clientConfig.getMqClientApiTimeout()); if (!producerTable.isEmpty()) { TopicPublishInfo publishInfo = topicRouteData2TopicPublishInfo(topic, topicRouteData); publishInfo.setHaveTopicRouterInfo(true ); Iterator<Entry<String, MQProducerInner>> it = this .producerTable.entrySet().iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { Entry<String, MQProducerInner> entry = it.next(); MQProducerInner impl = entry.getValue(); if (impl != null ) { impl.updateTopicPublishInfo(topic, publishInfo); } } }
更新逻辑⽐较简单,⾸先从名字服务获取主题路由信息对象 topicRoute ,然后更新 DefaultMQProducerImpl 的主题发布信息 topicPublishInfoTable 对象 。
2.3 发送消息 进⼊ DefaultMQProducerImpl 类,查看发送消息⽅法 sendDefaultImpl 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this .tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(msg.getTopic());int timesTotal = communicationMode == CommunicationMode.SYNC ? 1 + this .defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendFailed() : 1 ;for (; times < timesTotal; times++) { String lastBrokerName = null == mq ? null : mq.getBrokerName(); MessageQueue mqSelected = this .selectOneMessageQueue(topicPublishInfo, lastBrokerName); if (mqSelected != null ) { mq = mqSelected; brokersSent[times] = mq.getBrokerName(); try { beginTimestampPrev = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (times > 0 ) { msg.setTopic(this .defaultMQProducer.withNamespace(msg.getTopic())); } long costTime = beginTimestampPrev - beginTimestampFirst; if (timeout < costTime) { callTimeout = true ; break ; } sendResult = this .sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, timeout - costTime); endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false ); switch (communicationMode) { case ASYNC: return null ; case ONEWAY: return null ; case SYNC: if (sendResult.getSendStatus() != SendStatus.SEND_OK) { if (this .defaultMQProducer.isRetryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK()) { continue ; } } return sendResult; default : break ; } } catch (RemotingException e) { endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true ); log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, resend at once, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s" , invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mq), e); log.warn(msg.toString()); exception = e; continue ; } catch (MQClientException e) { endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true ); log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, resend at once, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s" , invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mq), e); log.warn(msg.toString()); exception = e; continue ; } catch (MQBrokerException e) { endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true ); log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, resend at once, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s" , invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mq), e); log.warn(msg.toString()); exception = e; if (this .defaultMQProducer.getRetryResponseCodes().contains(e.getResponseCode())) { continue ; } else { if (sendResult != null ) { return sendResult; } throw e; } } catch (InterruptedException e) { endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false ); log.warn(String.format("sendKernelImpl exception, throw exception, InvokeID: %s, RT: %sms, Broker: %s" , invokeID, endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, mq), e); log.warn(msg.toString()); log.warn("sendKernelImpl exception" , e); log.warn(msg.toString()); throw e; } } else { break ; } } if (sendResult != null ) { return sendResult; }
将发送消息流程简化如下:
获取主题发布信息;
根据路由算法选择⼀个消息队列,也就是 selectOneMessageQueue ⽅法;
调⽤ sendKernelImpl 发放消息对象,封装成发送结果对象 sendResult 。
2.3.1 尝试获取主题发布信息 我们知道 MQClientInstance 的定时任务每隔30秒会更新⽣产者实现类的 topicPublishInfoTable ,但若第⼀次发送消息时,若缓存中⽆数据时候,还是要重新拉取⼀次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private TopicPublishInfo tryToFindTopicPublishInfo (final String topic) { TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this .topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic); if (null == topicPublishInfo || !topicPublishInfo.ok()) { this .topicPublishInfoTable.putIfAbsent(topic, new TopicPublishInfo ()); this .mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic); topicPublishInfo = this .topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic); } if (topicPublishInfo.isHaveTopicRouterInfo() || topicPublishInfo.ok()) { return topicPublishInfo; } else { this .mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, true , this .defaultMQProducer); topicPublishInfo = this .topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic); return topicPublishInfo; } }
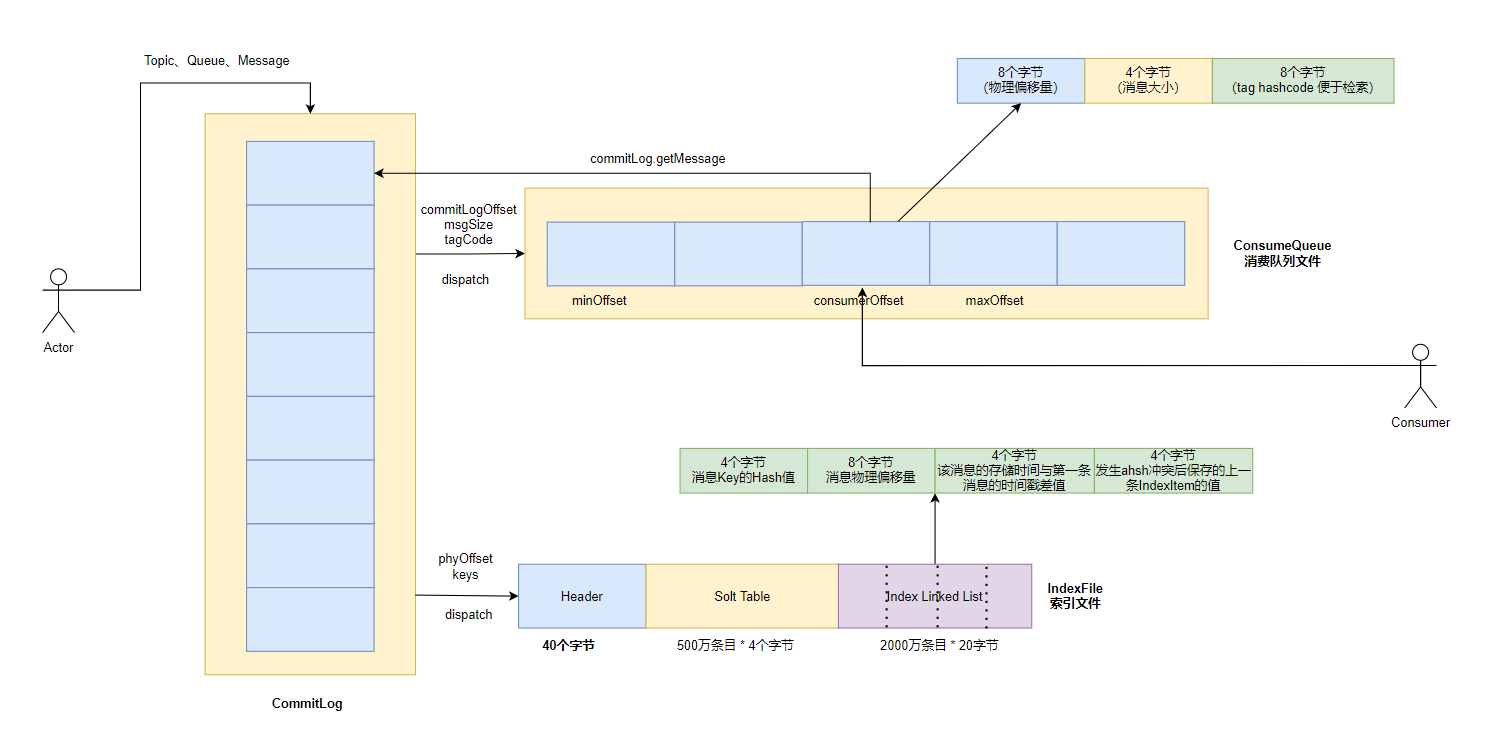
2.3.2 根据路由算法选择一个消息队列 RocketMQ 存储模型包含三部分: 数据⽂件 commitlog 、消费⽂件 consumequeue 、索引⽂件 indexfile。
因此根据 RocketMQ 的存储模型设计,对于⽣产者来讲,发送消息时,必须指定该主题对应的队列。路由算法,我们会在路由机制这⼀节重点讲解。
1 MessageQueue mqSelected = this .selectOneMessageQueue(topicPublishInfo, lastBrokerName);
2.3.3 调用实例客户端API发送消息 通过路由机制选择⼀个 messageQueue 之后,调⽤实例客户端 API 发送消息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 String brokerAddr = this .mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInPublish(mq.getBrokerName());sendResult = this .mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().sendMessage( brokerAddr, mq.getBrokerName(), tmpMessage, requestHeader, timeout - costTimeAsync, communicationMode, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, this .mQClientFactory, this .defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendAsyncFailed(), context, this );
Broker 端在收到发送消息请求后,调⽤处理器 SendMessageProcessor 处理请求,处理完成后,将响应结果返回给⽣产者客户端,客户端将接收到的数据组装成 SendResult 对象。
3. 路由机制 进⼊ DefaultMQProducerImpl#selectOneMessageQueue ⽅法:
1 2 3 public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue (final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) { return this .mqFaultStrategy.selectOneMessageQueue(tpInfo, lastBrokerName); }
路由机制通过调⽤ MQFaultStrategy 的 selectOneMessageQueue ⽅法 ,这⾥有⼀个 sendLatencyFaultEnable 开关变量,默认为 false 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 public class MQFaultStrategy { private final static InternalLogger log = ClientLogger.getLog(); private final LatencyFaultTolerance<String> latencyFaultTolerance = new LatencyFaultToleranceImpl (); private boolean sendLatencyFaultEnable = false ; private long [] latencyMax = {50L , 100L , 550L , 1000L , 2000L , 3000L , 15000L }; private long [] notAvailableDuration = {0L , 0L , 30000L , 60000L , 120000L , 180000L , 600000L }; public long [] getNotAvailableDuration() { return notAvailableDuration; } public void setNotAvailableDuration (final long [] notAvailableDuration) { this .notAvailableDuration = notAvailableDuration; } public long [] getLatencyMax() { return latencyMax; } public void setLatencyMax (final long [] latencyMax) { this .latencyMax = latencyMax; } public boolean isSendLatencyFaultEnable () { return sendLatencyFaultEnable; } public void setSendLatencyFaultEnable (final boolean sendLatencyFaultEnable) { this .sendLatencyFaultEnable = sendLatencyFaultEnable; } public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue (final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) { if (this .sendLatencyFaultEnable) { try { int index = tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().incrementAndGet(); for (int i = 0 ; i < tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size(); i++) { int pos = Math.abs(index++) % tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size(); if (pos < 0 ) pos = 0 ; MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().get(pos); if (latencyFaultTolerance.isAvailable(mq.getBrokerName())) return mq; } final String notBestBroker = latencyFaultTolerance.pickOneAtLeast(); int writeQueueNums = tpInfo.getQueueIdByBroker(notBestBroker); if (writeQueueNums > 0 ) { final MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(); if (notBestBroker != null ) { mq.setBrokerName(notBestBroker); mq.setQueueId(tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().incrementAndGet() % writeQueueNums); } return mq; } else { latencyFaultTolerance.remove(notBestBroker); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("Error occurred when selecting message queue" , e); } return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(); } return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(lastBrokerName); } public void updateFaultItem (final String brokerName, final long currentLatency, boolean isolation) { if (this .sendLatencyFaultEnable) { long duration = computeNotAvailableDuration(isolation ? 30000 : currentLatency); this .latencyFaultTolerance.updateFaultItem(brokerName, currentLatency, duration); } } private long computeNotAvailableDuration (final long currentLatency) { for (int i = latencyMax.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { if (currentLatency >= latencyMax[i]) return this .notAvailableDuration[i]; } return 0 ; } }
这⾥有两个逻辑分⽀ :
sendLatencyFaultEnable 为 false ,通过 TopicPublishInfo 中的 messageQueueList 中选择⼀个队列 (MessageQueue)进⾏发送消息 ;
sendLatencyFaultEnable 为 true ,开启延迟容错机制。
3.1 默认机制 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue (final String lastBrokerName) { if (lastBrokerName == null ) { return selectOneMessageQueue(); } else { for (int i = 0 ; i < this .messageQueueList.size(); i++) { int index = this .sendWhichQueue.incrementAndGet(); int pos = Math.abs(index) % this .messageQueueList.size(); if (pos < 0 ) pos = 0 ; MessageQueue mq = this .messageQueueList.get(pos); if (!mq.getBrokerName().equals(lastBrokerName)) { return mq; } } return selectOneMessageQueue(); } } public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue () { int index = this .sendWhichQueue.incrementAndGet(); int pos = Math.abs(index) % this .messageQueueList.size(); if (pos < 0 ) pos = 0 ; return this .messageQueueList.get(pos); }
默认机制有两个要点:
循环遍历该主题下所有的队列 ;
若上⼀个失败的 Broker 参数值存在,需要过滤掉上⼀个失败的 Broker 。
3.2 延迟容错机制 所谓延迟容错机制,是指发送消息时,若某个队列对应的 Broker 宕机了,在默认机制下很可能下⼀次选择的队列还是在已经宕机的 broker ,没有办法规避故障的broker,因此消息发送很可能会再次失败,重试发送造成了不必要的性能损失。
因此 producer 提供了延迟容错机制来规避故障的 Broker 。
当 sendLatencyFaultEnable 开关为 true 时,在随机递增取模的基础上,代码逻辑会再去过滤掉 not available 的 Broker 。
1 2 if (latencyFaultTolerance.isAvailable(mq.getBrokerName())) return mq;
所谓的” latencyFaultTolerance “,是指对之前失败的,按⼀定的时间做退避。
例如,如果上次请求的latency超过 550Lms,就退避 3000Lms;超过1000L,就退避 60000L ;如果关闭,采⽤随机递增取模的⽅式选择⼀个队列(MessageQueue)来发送消息, latencyFaultTolerance 机制是实现消息发送⾼可⽤的核⼼关键所在。
1 2 3 4 sendResult = this .sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, timeout - costTime); endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false );
发送消息时捕捉到异常同样会调⽤ updateFaultItem ⽅法:
1 2 endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true );
endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev 等于消息发送耗时,如果成功发送第三个参数传的是 false ,发送失败传 true。
继续查看 MQFaultStrategy#updateFaultItem 源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public void updateFaultItem (final String brokerName, final long currentLatency, boolean isolation) { if (this .sendLatencyFaultEnable) { long duration = computeNotAvailableDuration(isolation ? 30000 : currentLatency); this .latencyFaultTolerance.updateFaultItem(brokerName, currentLatency, duration); } } private long computeNotAvailableDuration (final long currentLatency) { for (int i = latencyMax.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { if (currentLatency >= latencyMax[i]) return this .notAvailableDuration[i]; } return 0 ; }
computeNotAvailableDuration ⽅法会判断当前消息发送耗时,位于哪⼀个延迟级别,然后选择对应的 duration 。
1 2 private long [] latencyMax = {50L , 100L , 550L , 1000L , 2000L , 3000L , 15000L };private long [] notAvailableDuration = {0L , 0L , 30000L , 60000L , 120000L , 180000L , 600000L };
如果 isolation 为 true,该 broker 会得到⼀个10分钟规避时⻓ ,也就是 600000L 毫秒 。
如果 isolation 为 false,假设 currentLatency 为 600L , 那么规避时间 30000L 毫秒。
查看 LatencyFaultToleranceImpl#updateFaultItem 源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public void updateFaultItem (final String name, final long currentLatency, final long notAvailableDuration) { FaultItem old = this .faultItemTable.get(name); if (null == old) { final FaultItem faultItem = new FaultItem (name); faultItem.setCurrentLatency(currentLatency); faultItem.setStartTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis() + notAvailableDuration); old = this .faultItemTable.putIfAbsent(name, faultItem); if (old != null ) { old.setCurrentLatency(currentLatency); old.setStartTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis() + notAvailableDuration); } } else { old.setCurrentLatency(currentLatency); old.setStartTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis() + notAvailableDuration); } }
FaultItem 为存储故障 broker 的类,称为失败条⽬,每个条⽬存储了 broker 的名称、消息发送延迟时⻓、故障规避开始时间。
该⽅法主要是对失败条⽬的⼀些更新操作,如果失败条⽬已存在,那么更新失败条⽬,如果失败条⽬不存在,那么新建失败条⽬,其中失败条⽬的 startTimestamp 为当前系统时间加上规避时⻓, startTimestamp 是判断 broker 是否可⽤的时间值:
1 2 3 public boolean isAvailable () { return (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTimestamp) >= 0 ; }
4. 顺序消息 顺序消息可以保证消息的消费顺序和发送的顺序⼀致,即先发送的先消费,后发送的后消费,常⽤于⾦融证券、电商业务等对消息指令顺序有严格要求的场景。
4.1 如何保证顺序消息 消息的顺序需要由以下三个阶段保证:
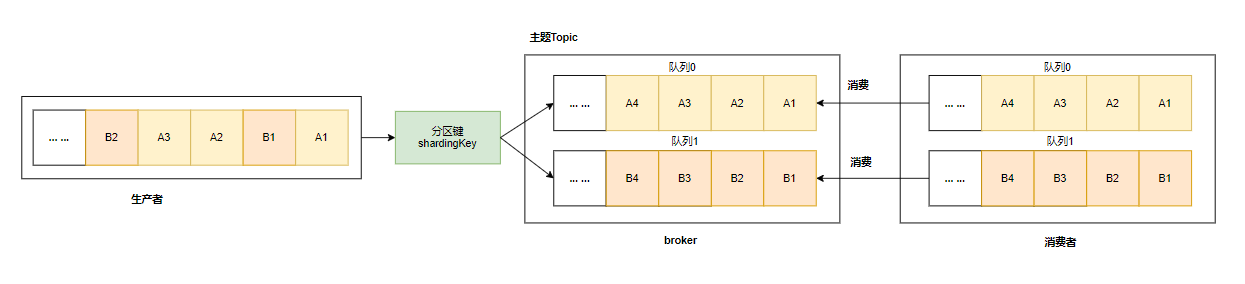
如上图所示,A1、B1、A2、A3、B2、B3 是订单 A 和订单 B 的消息产⽣的顺序,业务上要求同⼀订单的消息保持 顺序,例如订单A的消息发送和消费都按照 A1、A2、A3 的顺序。
如果是普通消息,订单A的消息可能会被轮询发送到不同的队列中,不同队列的消息将⽆法保持顺序,⽽顺序消息发送时 RocketMQ ⽀持将 Sharding Key 相同(例如同⼀订单号)的消息序路由到⼀个队列中 。
RocketMQ 服务端判定消息产⽣的顺序性是参照同⼀⽣产者发送消息 的时序。不同⽣产者、不同线程并发产⽣的消息,云消息队列 RocketMQ 版服务端⽆法判定消息的先后顺序。
顺序消息的 Topic 中,每个逻辑队列对应⼀个物理队列,当消息按照顺序发送到 Topic 中的逻辑队列时,每个分区的消息将按照同样的顺序存储到对应的物理队列中。
对于 kafka 来讲,1个主题会有多个分区,数据存储在每个分区,分区⾥⽂件以 Segment ⽂件串联起来。 对于 RocketMQ 来讲 , 存储模型包含三部分: 数据⽂件 commitlog 、消费⽂件 consumequeue 、索引⽂件 indexfile 。
kafka 和 RocketMQ ⽂件模型很类似,只不过 kafka 的⽂件数据都会存储在不同的分区⾥,⽽ RocketMQ 的数据都 存储在 CommitLog ⽂件⾥ ,不同的消息会存储在不同的消费队列⽂件⾥,便于提升消费者性能(索引)。
所以我们只需要将特定的消息发送到特定的逻辑队列⾥,对于 kafka 来讲是分区 partition ,对于 RocketMQ 来讲,就是消费队列 messageQueue 。
RocketMQ 按照存储的顺序将消息投递给 Consumer,Consumer 收到消息后也不对消息顺序做任何处理,按照接收到的顺序进⾏消费。
Consumer 消费消息时,同⼀ Sharding Key 的消息使⽤单线程消费,保证消息消费顺序和存储顺序⼀致,最终实现消费顺序和发布顺序的⼀致。
4.2 生产者发送顺序消息 生产者发送顺序消息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer ("please_rename_unique_group_name" );producer.start(); String[] tags = new String [] {"TagA" , "TagB" , "TagC" , "TagD" , "TagE" }; for (int i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++) { int orderId = i % 10 ; Message msg = new Message ("TopicTestjjj" , tags[i % tags.length], "KEY" + i, ("Hello RocketMQ " + i).getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET)); SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg, new MessageQueueSelector () { @Override public MessageQueue select (List<MessageQueue> mqs, Message msg, Object arg) { Integer id = (Integer) arg; int index = id % mqs.size(); return mqs.get(index); } }, orderId); System.out.printf("%s%n" , sendResult); } producer.shutdown();
发送顺序消息需要定制队列选择器 MessageQueueSelector 。
1 2 3 4 5 SendResult send (final Message msg, final MessageQueueSelector selector, final Object arg) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException;public interface MessageQueueSelector {MessageQueue select (final List<MessageQueue> mqs, final Message msg, final Object arg) ; }
进⼊ DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendSelectImpl , 查看顺序消费发送的实现逻辑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 private SendResult sendSelectImpl ( Message msg, MessageQueueSelector selector, Object arg, final CommunicationMode communicationMode, final SendCallback sendCallback, final long timeout ) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException { long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .makeSureStateOK(); Validators.checkMessage(msg, this .defaultMQProducer); TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this .tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(msg.getTopic()); if (topicPublishInfo != null && topicPublishInfo.ok()) { MessageQueue mq = null ; try { List<MessageQueue> messageQueueList = mQClientFactory.getMQAdminImpl().parsePublishMessageQueues(topicPublishInfo.getMessageQueueList()); Message userMessage = MessageAccessor.cloneMessage(msg); String userTopic = NamespaceUtil.withoutNamespace(userMessage.getTopic(), mQClientFactory.getClientConfig().getNamespace()); userMessage.setTopic(userTopic); mq = mQClientFactory.getClientConfig().queueWithNamespace(selector.select(messageQueueList, userMessage, arg)); } catch (Throwable e) { throw new MQClientException ("select message queue threw exception." , e); } long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime; if (timeout < costTime) { throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException ("sendSelectImpl call timeout" ); } if (mq != null ) { return this .sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, null , timeout - costTime); } else { throw new MQClientException ("select message queue return null." , null ); } } validateNameServerSetting(); throw new MQClientException ("No route info for this topic, " + msg.getTopic(), null ); }
从上⾯的顺序消息发送代码,我们得到两点结论:
顺序消息发送时,需要实现 MessageQueueSelector 的 select ⽅法 ;
发送顺序消息时,若发送失败没有重试。
参考:
RocketMQ消息发送的高可用设计-阿里云开发者社区 (aliyun.com)